Identification and Life Cycle
The house fly (musca domestica) is the most common household pest. Not only are house flies a nuisance, but they can transport disease causing organisms to humans and can be a public health problem.
The House flyis 3/16 to 1/4 – inch in size, with robust bodies, reddish eyes and two transparent wings. The thorax is marked with four narrow dark sripes. Their mouth parts are adapted for sponging up liquids, and cannot bite.
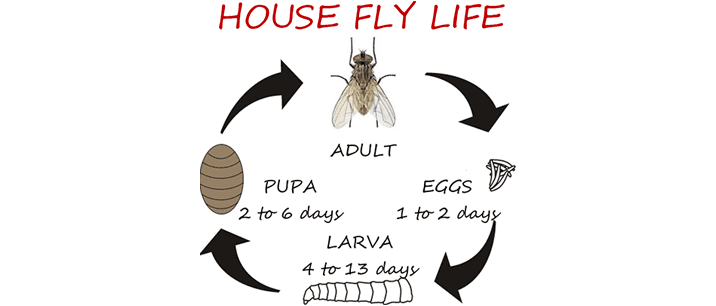
The female can lay up to 500 eggs in several groups of 75 to 150 eggs over a 3 to 4 day period. In as little as 1 to 2 days the worm-like maggots (larva) emerge from the eggs. They have no eyes, antennae or legs, and will feed on the material which they were layed upon. The larva goes through three instars (larval molts) to become a full-grown cream colored maggot in 4 to 13 days. They then form a reddish brown pupal case around them, and complete their final development within 2 to 6 days. Once the adult flies emerge from its pupal case, it will mate within one to two days later. They can live up up to 15 to 21 days long.



Comments are closed.